![]()
Spring Chemistry Homework #4 Answer Key
Introduction to Quantum Chemistry
Oxtoby, Nachtrieb and Gillis: Chapter 15:
33. The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states:
![]()
Here, Dx is the uncertainty in position and Dp is the uncertainty in momentum. Since the problem asks for the minimum uncertainty in velocity (p = mv), we will treat the above as an equality. So,
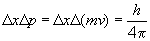
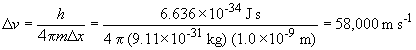
Thus, the velocity of this electron cannot be known to a precision more than ± 58,000 m/s.
b) The mass of a helium atom is given by:
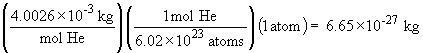
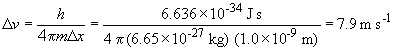
So the increased mass of the helium atom decreases the uncertainty of the velocity (but the uncertainty in momentum remains the same in a and b)
35. For the one dimensional particle in the box, the energy of the
particle is given by:
38.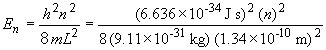
where,
h = Plank's constant
n = quantum level
m = mass of the electron
L = length of the box
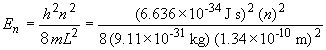
For n = 1, 2 and 3, the results are:
E1 = 3.37 × 10-18 J
E2 = 1.35 × 10-17 J
E3 = 3.03 × 10-17 JTo excite an electron from the ground state (E1) to the first excited state (E2) requires a photon with energy equal to E2 - E1, or 1.01 × 10-17 J. To find the wavelength, we do the following:
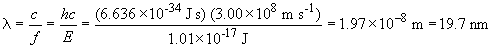
a) n = 3, l = 2, m = 1, ms = 0 Forbidden (ms cannot equal 0)
b) n = 2, l = 0, m = 0, ms = -½ Allowed (this is an electron in a 2s orbital)
c) n = 7, l = 2, m = -2, ms = ½ Allowed (this is an electron in a 7d orbital)
d) n = 3, l = -3, m = -2, ms = -½ Forbidden (l must be in the range: 0, 1, …n-1)
40/42.
| n | l | orbital | total nodes | radial nodes | angular nodes | |
| a | 3 | 2 | 3d | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| b | 7 | 4 | 7g | 6 | 2 | 4 |
| c | 5 | 1 | 5p | 4 | 3 | 1 |
44. The radial portion of the wavefunction for the 3p orbital is:
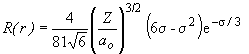
This term will equal zero only when s = 6. The definition of s, as given in Table 15.2 is:
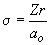
Therefore, when Z = 1, and ao = 0.529 Å,
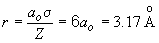
b) For the 3s orbital,
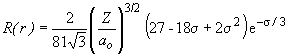
This function will equal zero only when s equals the roots of the quadratic term of the function. These are s = 3.8, 14.2. So the radii at which nodes occur are: 2.0 Å and 7.5 Å.
DeKock & Gray: Chapter 1:
13. For an electron in a 3d orbital, the following quantum numbers are possible:
n = 3 (only)
l = 2 (only)
m = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2