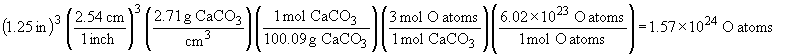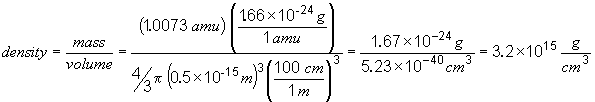
Review Assignment #2
Chapter 2
26.
a) carbon atoms in C2H5COOCH3: 4
b) oxygen atoms in Ca(ClO3)2: 6
c) hydrogen atoms in (NH4)2HPO4: 9
30.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38.
| Compound | Description | |
| a) | Sc2O3 | Ionic (Sc: metal, O: non-metal) |
| b) | NaI | Ionic (Na: metal, I: non-metal) |
| c) | SCl2 | Molecular (S: non-metal, Cl: non-metal) |
| d) | Ca(NO3)2 | Ionic (Ca: metal, NO3-: polyatomic anion) |
| e) | FeCl3 | Ionic (Fe: metal, Cl: non-metal) |
| f) | LaP | Ionic (La: metal, P: non-metal) |
| g) | CoCO3 | Ionic (Co: metal, CO32-: polyatomic anion) |
| h) | (NH4)2SO4 | Ionic (NH4+: polyatomic cation, SO42-: polyatomic anion) |
42. The following are ionic
compounds:
| Compound | Name | |
| a) | Ag2S | silver (I) sulfide |
| b) | Ba3(PO4)2 | barium phosphate |
| c) | Mg(ClO3)2 | magnesium chlorate |
| d) | SrSO3 | strontium sulfite |
| e) | CoBr2 | cobalt (II) bromide |
| f) | SnI2 | tin (II) iodide |
| g) | Cr(NO3)3 | chromium (III) nitrate |
| h) | ZnHPO4 | zinc (II) hydrogen phosphate |
| i) | AgClO4 | silver (I) perchlorate |
| j) | (NH4)2Cr2O7 | ammonium dichromate |
48.
| Compound | Name | |
| a) | N2O | dinitrogen monoxide |
| b) | NO | nitrogen monoxide |
| c) | NO2 | nitrogen dioxide |
| d) | N2O5 | dinitrogen pentoxide |
| e) | N2O4 | dinitrogen tetroxide |
54.
This is a huge density!
Chapter 3
6.
| a) | KNO3® KNO2 + ½ O2 |
| b) | La2O3 + 3 H2O ® 2 La(OH)3 |
| c) | NCl3 + 3 H2O ® NH3 + 3 HOCl |
| d) | Mg3N2 + 8 HCl ® 3 MgCl2 + 2 NH4Cl |
| e) | 2 AgNO3 + K2SO4 ® Ag2SO4 + 2 KNO3 |
| f) | 2 Al(OH)3 + 3 H2SO4 ® Al2(SO4)3 + 6 H2O |
| g) | 2 CH3NH2 + 9/2 O2 ® 2 CO2 + 5 H2O + N2 |
8.
c) 4 PH3 (g) + 8 O2 (g) ® 6 H2O (g) + P4O10 (s)d) Hg(NO3)2 (s) ® HgO (s) + 2 NO2 (g) + ½ O2 (g)
10 a) When a
hydrocarbon burns in air, O2 is the reactant involved in addition
to the hydrocarbon. For example, when benzene (C6H6)
burns, the reaction is:
C6H6 (l) + 15/2 O2 (g) ® 6 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (g)
b) When metallic sodium reacts with iodine, the reaction is:Na (s) + ½ I2 (s) ® NaI (s)
The product can be assumed to be a solid since it is an ionic compound (it consists of a metal and a non-metal).
18. The average atomic mass of
any element is the weighted average of the naturally occurring isotopes.
Therefore, for magnesium:
(0.7870) (23.98504)20. Formula weights:+ (0.1013) (24.98584)
+ (0.1117) (25.98259)
24.30955
c) Mg(OH)2: 58.319 amud) (NH2)2CO: 60.055 amu
e) CH3CO2C5H11: 130.184 amu
32.
This is very close (73 %) to the mass of the Earth.
36.
| a) | |
| b) | |
| c) | |
| d) |
38.
| a) | 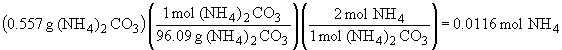 |
| b) | 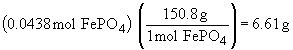 |
| c) |  |
| d) |
40.
| a) | 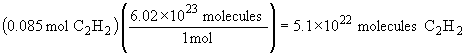 |
| b) | 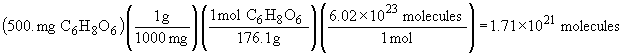 |
| c) | 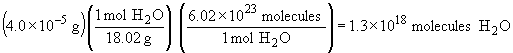 |
84. a) Moles of C is 1.25 carat diamond:
Atoms in 1.25 carat diamond:
b) Moles of aspirin in 0.500 g tablet:
Molecules in 0.500 g tablet:
103.