File:Frog and tad.jpg
From Comparative Physiology of Vision
Size of this preview: 738 × 600 pixels
Full resolution (1,654 × 1,344 pixels, file size: 934 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
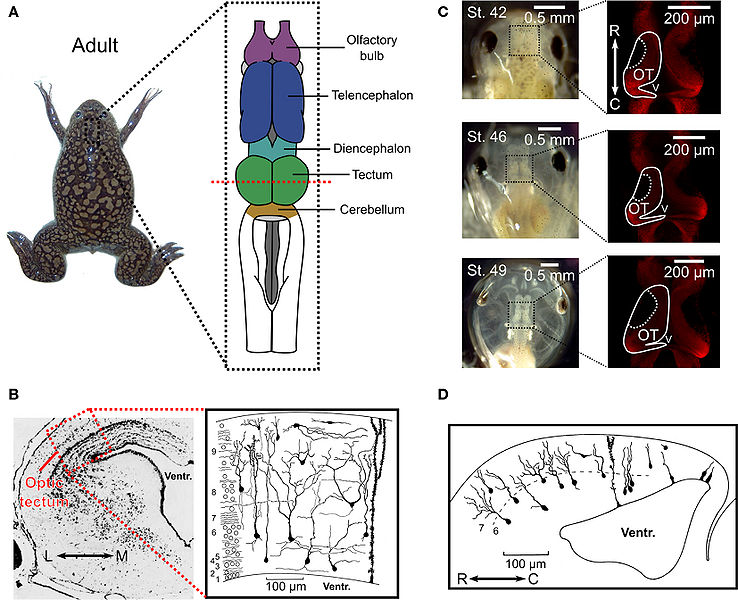
Anatomy of the optic tectum in the adult Xenopus laevis and during tadpole development. (A) In the adult Xenopus laevis frog (photograph) the central nervous system (drawing) contains several distinct structures and the optic tectum is the roof of the large midbrain structure, situated caudally to the diencephalon and rostrally to the cerebellum. It is one of the largest dorsal structures in the Xenopus brain, along with the telencephalon and the olfactory bulb. (B) The layered structure of the adult optic tectum can be seen in the coronal section (left), which has been stained with cresyl-violet. The section is taken from the plane indicated by the red dashed line in (A). As the drawing illustrates (right), there are several distinct cellular morphologies found within the optic tectum, which have been classified into 14 categories. The numbers at the side of the drawing indicate the 9 different layers of the tectum. (C) Photographs (left) of Xenopus laevis tadpoles taken dorsally at stages 42, 46, and 49 illustrate the changes that occur during the stages in which STDP is typically studied. During this time the optic tectum grows, as shown by confocal images of whole-mount brains with propidium iodide staining for cell nuclei. The images shown are in the horizontal plane and at a depth of 100 μm from the dorsal surface of the brain (right). Note the dark regions in the rostral–lateral optic tectum which are comprised mostly of neuropil. Neurogenesis takes place in the caudal–medial region surrounding the ventricle. (D) Due to the location of the neurogenerative zone there is a progression in the maturity and morphological complexity of cells in the optic tectum at these ages in the caudal–rostral axis, as shown by this camera lucida drawing of a sagittal slice from a stage 49 tadpole. Images in (B) and (D) are reproduced with permission from Lázár (1973) and Nikundiwe and Nieuwenhuys (1983).
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
(Latest | Earliest) View (newer 500) (older 500) (20 | 50 | 100 | 250 | 500)| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 01:31, 5 December 2011 |  | 1,654×1,344 (934 KB) | Quimac19 (Talk | contribs) | (Anatomy of the optic tectum in the adult Xenopus laevis and during tadpole development. (A) In the adult Xenopus laevis frog (photograph) the central nervous system (drawing) contains several distinct structures and the optic tectum is the roof of the lar) |
- Edit this file using an external application (See the setup instructions for more information)
File links
The following page links to this file:
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Width | 3307 |
|---|---|
| Height | 2687 |
| Compression scheme | Uncompressed |
| Pixel composition | RGB |
| Orientation | Normal |
| Number of components | 3 |
| Horizontal resolution | 300 dpi |
| Vertical resolution | 300 dpi |
| Data arrangement | chunky format |
| Software used | Adobe Photoshop CS2 Windows |
| File change date and time | 14:49, 16 June 2010 |
| Color space | 65535 |
